
If no subnetting is applied, the range of IP addresses and the standard subnet mask for the following classes will be:Ĭlass B = 128.0.x.x .x 255.255.0.0Ĭlass C = 192.0.0.x 255.255.255.0 Depending on the amount of necessary hosts or networks and the expected growth of your network, make your choice from these three classes. Class A has little room for networks, but many hosts, Class B is balanced in networks and hosts and Class C has a lot of networks and little room for hosts. When setting up a network, it is important to choose the right IP Class. The ID 127 is used as 'local hosts' or the 'loopback address'. If you look really good, you will see that 127.x.x.x is not a part of the classification of the IP address. In short, for a Class A network the first octet represents the network part, for a Class B the first two octets and for a Class C the first three octets. To accommodate different network sizes, IP address space was originally divided into three sections Class A (0.x.x.x to 126.x.x.x) - 8 bit network prefix or the first octet, Class B (128.0.x.x to .x) - 16 bit network prefix or the first two octets and Class C (192.0.0.x to ) - 24 bit network prefix or the first three octets.

#Class b subnet mask table 32 bit
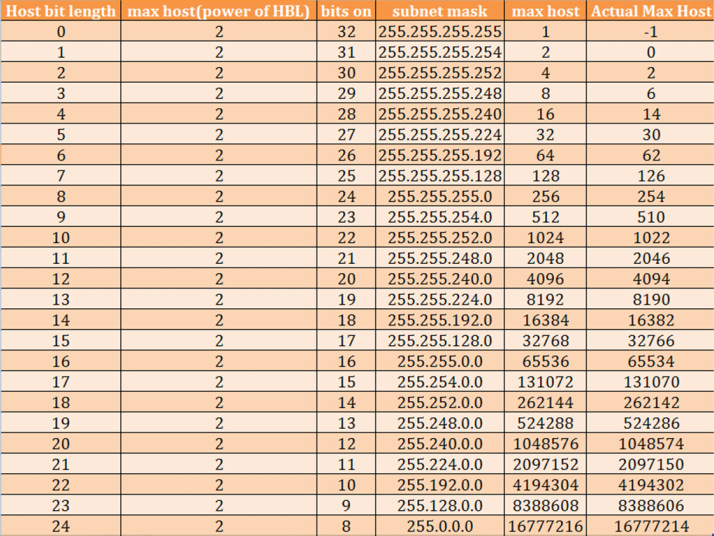
The first part of each 32 bit number represents the network, and the remaining part refers to the individual computer (x) or the hosts.

Look at the following table to view the different classes. The value of the first octet determines the type of class. To understand IP classes, you need to understand that every IP address consists of 4 octets, 8 bits each.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
